Heated-Up Softmax Embedding
This work is performed at Digital Video Multimedia Lab at Columbia University and is supervised by Professor Shih-Fu Chang.
Overview
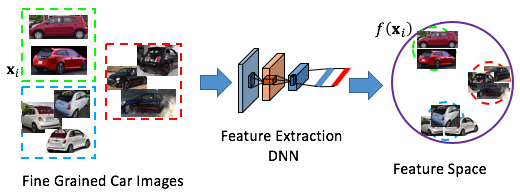
Metric Learning has become a popular topic in computer vision. In metrical learning, the goal is to learn from examples a similarity function that measures how similar two samples are. Ideally, the resulted algorithm learns such features that samples from the same class are placed as close as possible while samples from different classes are placed as far as possible. An example of such a pipeline can be viewed below.
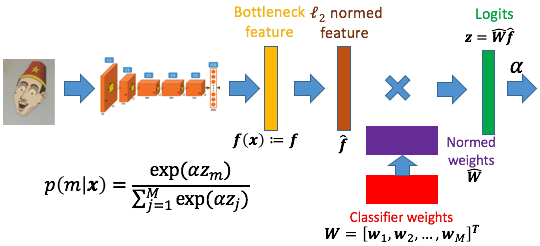
We propose a “heating-up” strategy to train a classifier with various temperatures. It can be divided into two parts. First of all, we train the proposed network based on classification error calculated by cross-entropy between softmax laye output and one-hot vector of ground truth. In addition, we apply $\ell_2$ normalization to both bottleneck features and their weights. Second, we vary temperature parameter $\alpha$ in softmax layer for gradient tuning.
The final framework can be viewed as:
Contributions
I joined the project since the beginning. My work mainly focuses on two parts. First of all, I unify the implementation of GoogLeNet V1 to Tensorflow instead of Caffe. To make sure the implementation is consistent, I dived into Caffe and Tensorflow framework and compared input and output of each layer in the model. I learned how different initiailizations, preprocessing, convolutional paddings and normalization would the final performance. Secondly, having implemented the model in Tensorflow, I reproduce the algorithm from the paper “No Fuss Distance Metric Learning using Proxies” and implement new ideas to generate reauls for comparisons.
| Platform | Ubuntu 16.04 |
| Programming Language | C++,Python,Matlab |
| Deep Learning Framework | Caffe, Tensorflow |
| Research Area | Computer Vision |
